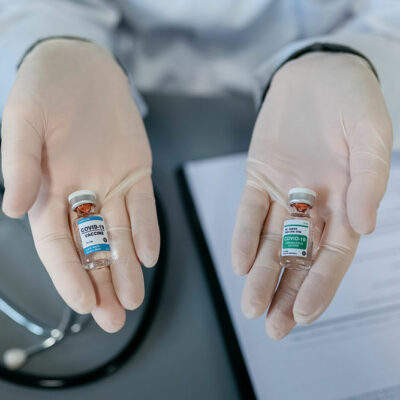
Here’s what makes Novavax an alternative to mRNA vaccines
When it comes to vaccine development, two innovative approaches have taken center stage in recent years—protein subunit (Novavax) and mRNA vaccines. Both are methods of bolstering immunity against infectious diseases, each with its own set of merits and considerations. To highlight the difference between both approaches, this article explores the characteristics of COVID-19 vaccines, highlighting what makes Novavax an alternative to mRNA vaccines in helping build immunity against the disease: Disease-specific considerations The nature of the infectious disease in question plays a pivotal role in determining which vaccine approach is most appropriate. In situations where rapid response is essential, such as the early stages of a pandemic, mRNA vaccines, with their shorter development timelines, may offer a distinct advantage. Here, the ability to swiftly generate and distribute these vaccines was evident in the last few years. On the other hand, for a targeted adaptation to emerging variants, Novavax’s adaptable protein subunit technology can be utilized. Here, the capability to accommodate evolving viral strains makes the vaccine part of the long-term vaccination strategy. Vaccine technology To understand the differences and similarities between Novavax and mRNA vaccines, here are the fundamental principles underlying these vaccine technologies. – The mRNA vaccines work by introducing a small piece of genetic material, called messenger RNA (mRNA), into the body.
Read Article